Refraktions
Current Version: 2.2.5 | Manual (PDF) | Demo videos
Introduction
Refraktions is an 8-track generative MIDI sequencer with artificial intelligence. Your taps imprint the AI memory and help it generate loops tailored to your choices over time. Start by tapping the screen in several places. Each tap triggers a sound. These sounds will loop and morph into new compositions over time, evolving indefinitely. More taps will be taken into consideration by AI and steer the app in new directions. The AI memory persists between app launches and the more you use the app, the more it learns about the tracks, pitches, and compositions you prefer, weighing your most recent decisions more heavily.
Conventions of this Manual
When referring to "your device", that can be an iPhone, iPad, or iPod touch with iOS 10.0 (arm64) or higher. There is not a Refraktions 2.x for Android at this point.
When referring to app settings, settings are indicated like this, and the value they are set to like this.
For example: Set the Background Mode to on.
System Requirements
Refraktions requires iOS 10.0 and an arm64 processor.
Quick Start
Inputting notes
Tap or sweep the screen to enter notes into the sequencer tracks. Each note plays the track's corresponding synthesizer sample. The left side is low, the right side is high.

The notes will loop, getting quieter each time it plays. When the note has completely faded out, the overall composition is assessed by the AI and new sequences are generated. The result is that each time the app is used it outputs a unique composition that morphs and evolves over time. The more the app is used, the more the AI shapes itself to the user.
Removing notes
To remove the notes on an individual track, swipe right in its zone.

Rearrange notes
To rearrange the notes on all tracks, shake your device.
Changing the Tempo
To get the Tempo Selector to appear, drag three fingers up or down the screen.
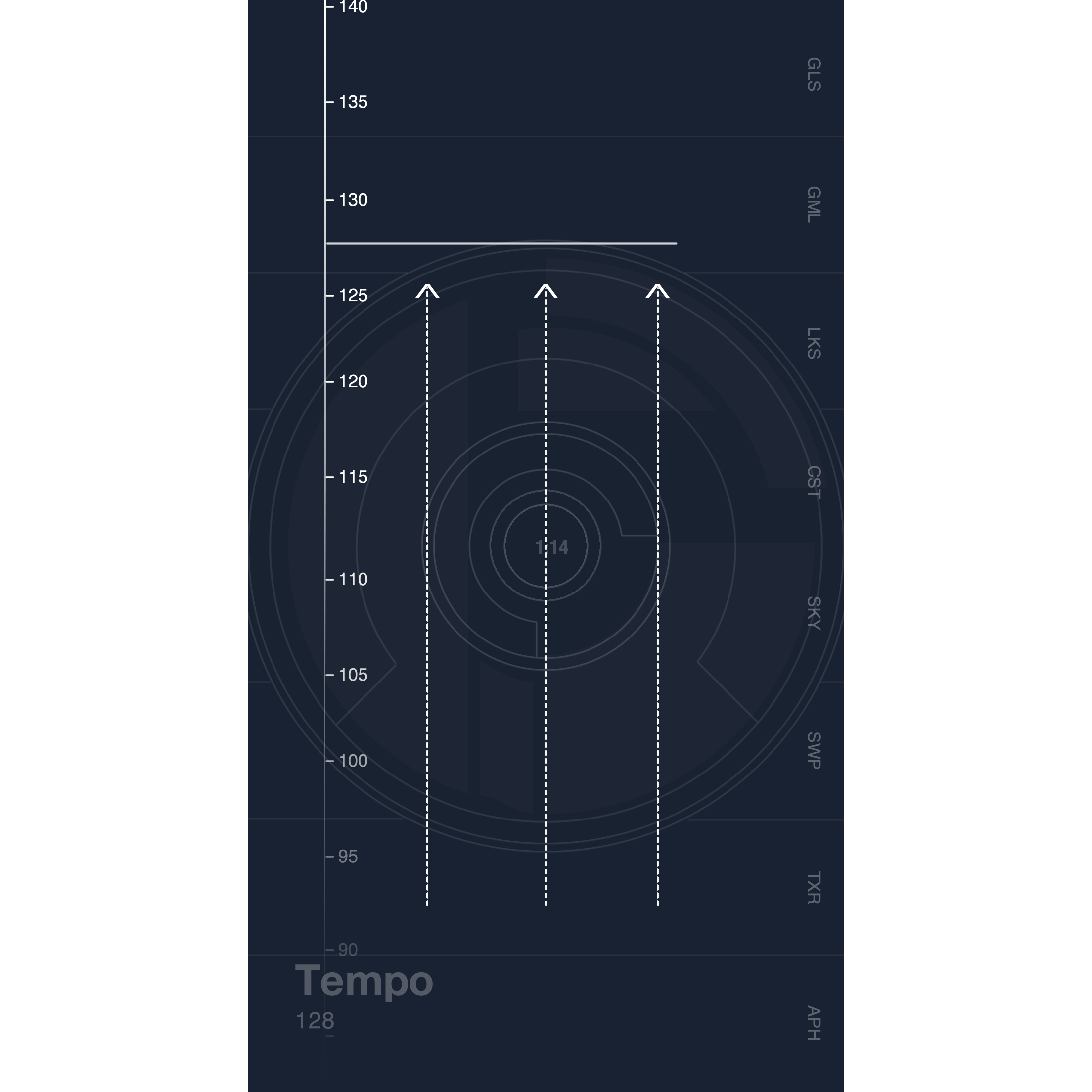
Note: This also changes the outgoing MIDI timing clock if MIDI Clock is set to Send MIDI Clock.
Scrubbing the sequencer
Emulating the jog-wheel on classic hardware MIDI sequencers, you can change the position of the playhead by spinning the outside ring of the sequencer circles. This action also sends the corresponding Song Position data to the MIDI Destinations.

Resetting the sequencer
To reset the sequencer, draw a counter-clockwise circle on the screen. This is an easy way to clear out a busy song and start from scratch. If MIDI Clock is set to Send MIDI Clock, then a MIDI Song Position of 0 0 is sent to the MIDI Destinations.

Note: This gesture does not move the internal sequencer back to 0 if MIDI Clock is set to Sync to External MIDI Clock or Ableton Link is enabled because the position is being controlled by an external device.
Randomize the sequencer
At any point, shake the device to rearrange the compostion on all tracks. This is a fast way to explore different compositions.
Release Notes
2.2.5
- Improvements to the AI for high density compositions.
- Improvements to Audiobus loading for Audiobus 3.3.1.
2.2.4
- Real-time note mapping to the user-selected octave and scale. Includes incoming MIDI notes from external sources.
- Added a customizable musical scale.
2.2.3
- Unused tracks can now be disabled and hidden, simplifying the interface.
2.2.2
- MIDI, Audiobus, and AUM integration bug fixes.
2.2.1
- Notes are easier to trigger on touches-moved, so screen acts more like a keyboard.
- Track volume slider now controls MIDI note velocty.
- Improved MIDI destination display on main screen and settings panel.
- Bug fixes for AUM and Audiobus loading.
- Music will continue to play during a locked screen when Background Mode is on.
2.2
- Audiobus 3.0.2 added. Refraktions is available as an Audio Source, MIDI Source, and MIDI Filter.
- App can now receive note input from external MIDI controllers or other iOS apps (as destination "Refraktions").
- Play / pause functionality added by tapping center circle.
- Added 8th synth, "Coastal Synth."
- Added ability to change root key in musical scales.
- Added per-track customization of playback, composition, volume, and pitch.
- Added global and per-track customization of MIDI sources and destinations.
- Added shake detection, which rearranges the composition.
- Improved note creation, including fixes to MIDI on / off for each tap.
- Rebuilt internal metronome with average drift variance of < 0.7 ms.
- Switch from UserDefaults to CoreData for data storage.
2.1.3
- Audiobus 2.3.2 added, all sounds routed to a single send port.
- Added 14 musical scales.
- Rebuilt audio engine for lower latency and future expandability.
- Rebuilt gesture recognizers for better control of tempo and jog wheel.
- Added right-swipe gesture to erase sounds of individual track.
- Improved AI to better reproduce user's composition density.
2.1.2
- Background Mode was added to the Settings Panel, allowing the app to play audio or send MIDI notes while in the background.
- MIDI Destinations was added to the Settings Panel, giving the user the option to choose specific, or multiple MIDI destinations, including other MIDI-enabled iOS apps.
2.1.1
- An artificial intelligence was added, complete with memory, the ability to learn the user's preferences, and generate new compositions based on that data.
- Sequencer jog-wheel was added, giving the user more control over the song position.
- MIDI Send toggle was replaced by MIDI Mode, simplifying the process of controlling external synthesizers.
- Ability to choose major or minor scale was added.
2.1
- Settings Panel was added inside the app for easier customization.
- Ableton Link was added, enabling Refraktions to sync with any other Ableton Link enabled device.
2.0
App Layout
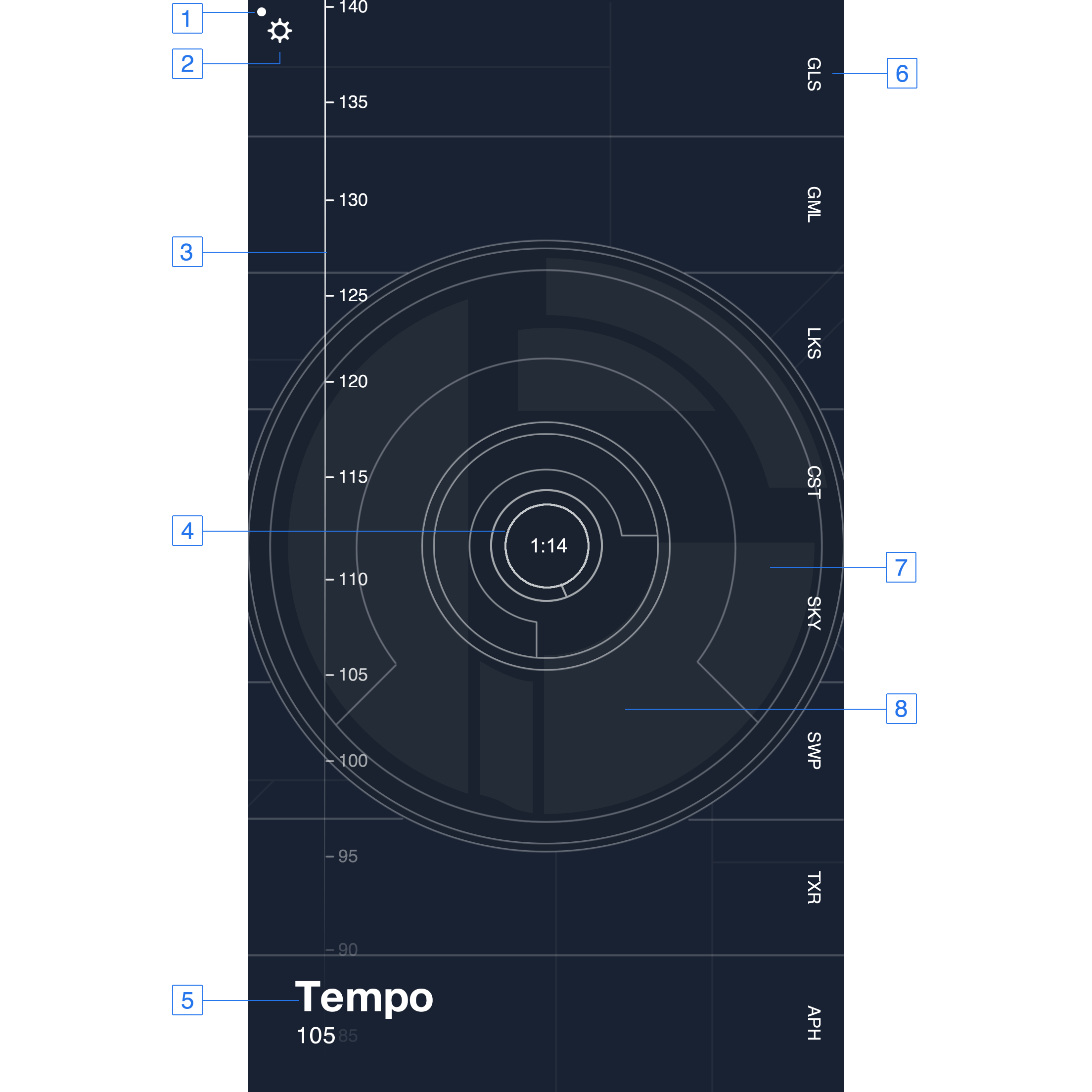
- MIDI Indication Light indicates when a MIDI note is being sent or received.
- Settings Button opens up the Settings Panel.
- Tempo Selector allows the user to change the app's internal tempo.
- Sequencer Position Display displays the current beat and bar of the internal sequencer.
- Text Display outputs various messages to the user.
- Tracks are the horizontal sections running from top to bottom of the screen. Tapping the tracks add notes into the sequencer loop.
- Jog wheel enables the user to scrub through the composition.
- Audio Mixer Overload Light is the set of dim white shapes behind the rotating circles. When the overall audio output of the app begins to peak, these shapes will get brighter.
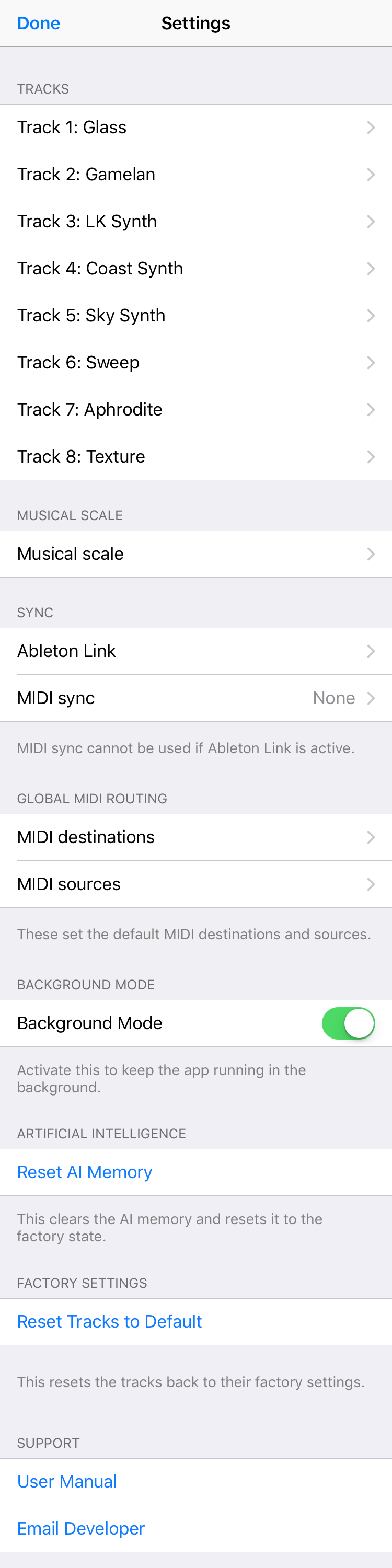
Settings Panel
Pressing the Settings Button (gear icon) opens the Settings Panel, which includes:
Tracks
Each track in the sequencer has attributes that can be customized.
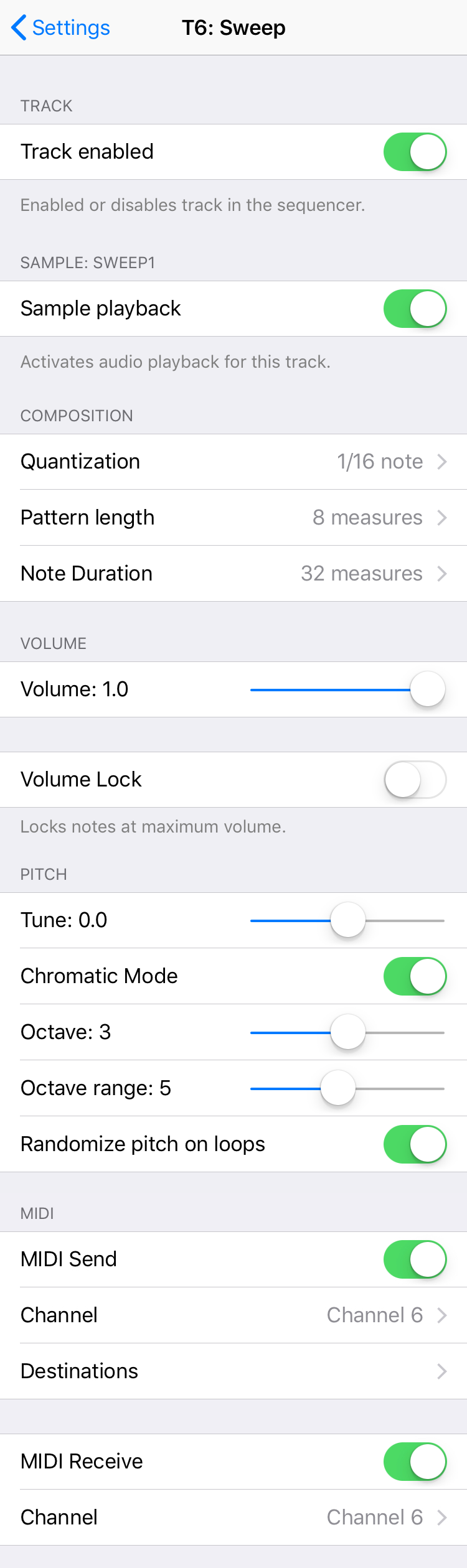
Sample Playback
The audio sample can be turned on or off for each track. Turn sample playback off to use the track for MIDI output only.
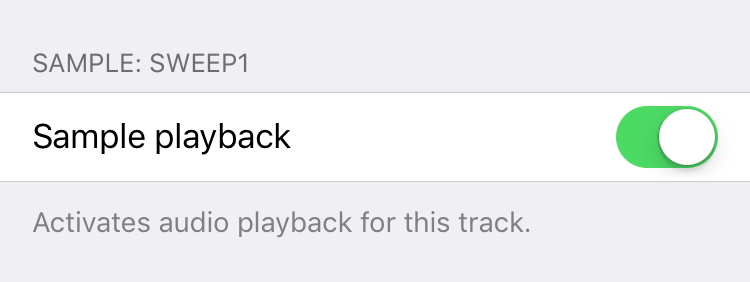
Composition
Quantization sets the increment that screen taps and MIDI controller notes are quantized to.
Pattern length is the number of measures in the track's loop.
Note duration is the number of measures it takes for a note to fade out and regenerate.
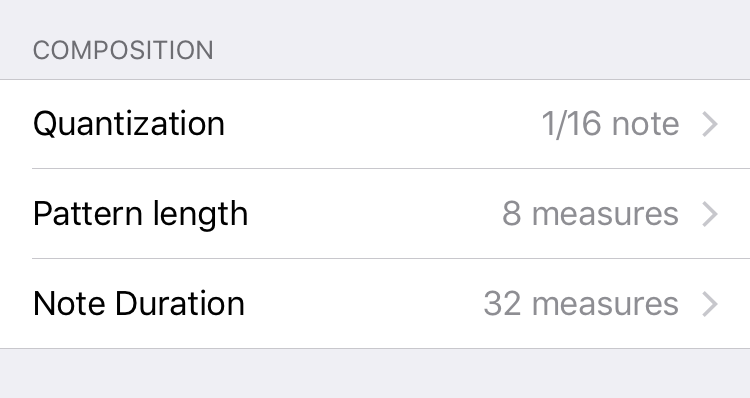
Volume
Volume sets the playback volume of the track.
Volume Lock prevents a sound from ever fading out, having the track act like a traditional, infinitely-looping MIDI sequencer.
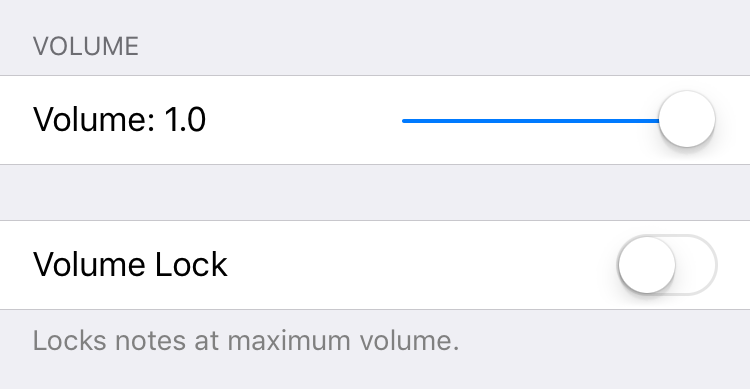
Pitch
Tune sets the playback pitch for every note in the track.
Chromatic Mode enables screen taps to input notes on a scale, rather than just middle C.
Note duration is the number of measures it takes for a note to fade out and regenerate.
Octave is center octave in the octave range.
Octave Range is the number of octaves accessible to screen touches for this track.
Randomize pitch on loops enables notes to shift up or down (still within scale) when they play in the sequencer loop.
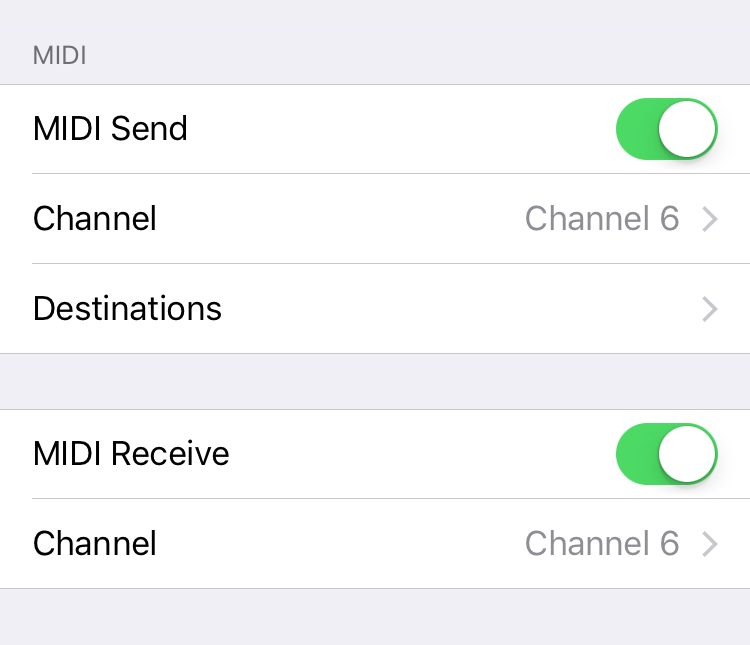
MIDI
MIDI Send enables notes on this track to be sent to the MIDI out port.
Channel determines the channel MIDI notes are sent on.
Destinations are the targets the MIDI note are sent to. Global defers to the Global MIDI Routing selections.
MIDI Receive enables external MIDI controllers to input notes into the Refraktions sequencer.
Channel determines the channel that incoming notes are accepted on.
Note: this section is not accessible when Audiobus is active.
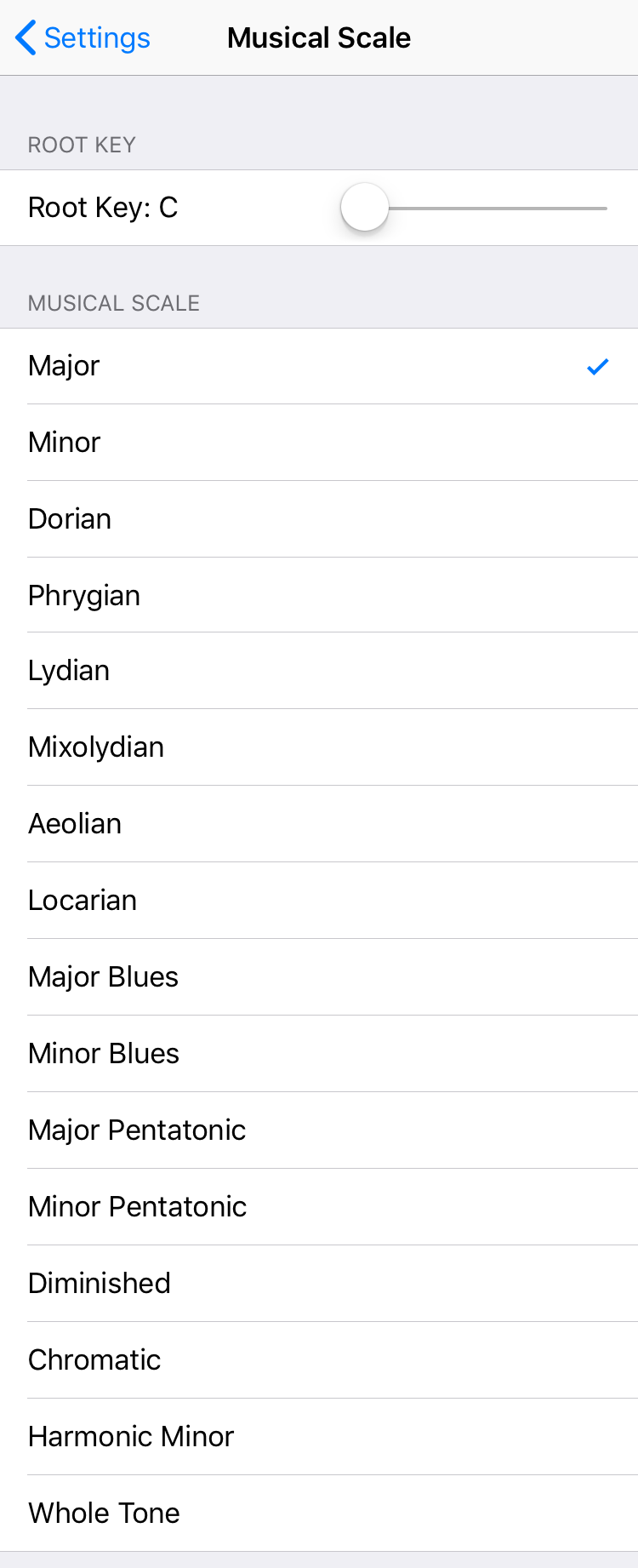
Musical Scale
Determines the musical scale and root key of the notes input via screen touches.
Sync
Either Ableton Link or MIDI can be used to sync Refraktions with other apps, software, or devices.
Note: this section is not accessible when Audiobus is active.
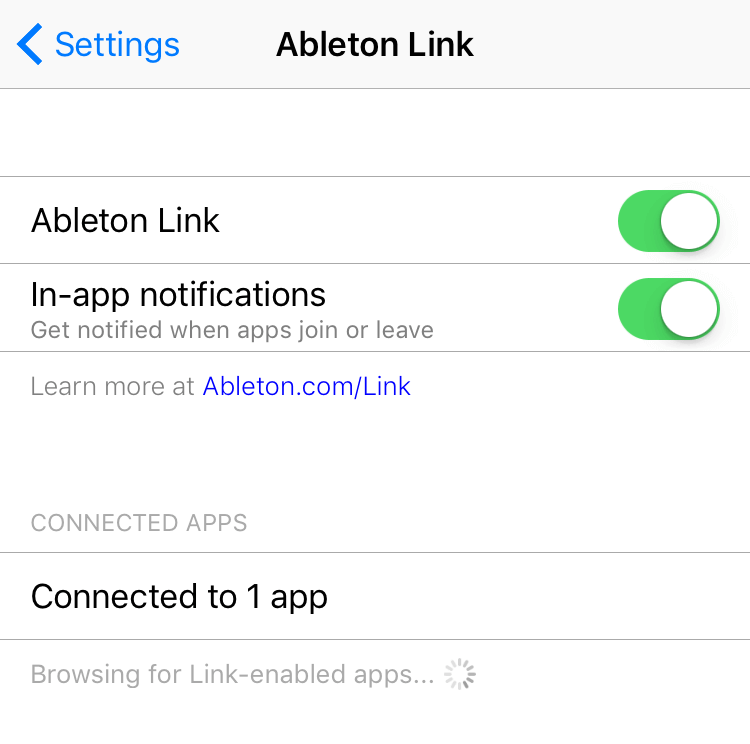
Ableton Link
Toggle for Ableton Link. This is automatically turned on when Audiobus is active. For more information about Link, see the Ableton Link website.
MIDI Sync
Select whether the app synchronizes to an external MIDI clock, sends a MIDI clock, or neither.
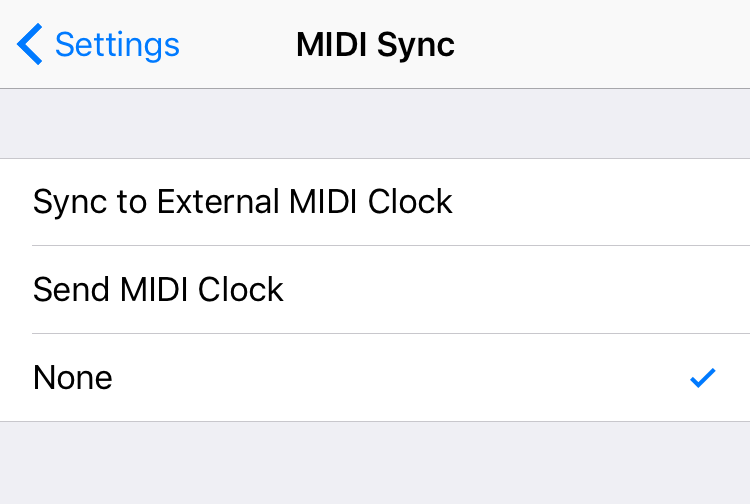
Sync to External MIDI Clock
Refraktions will listen for an external MIDI timing clock coming from another app, software DAW, or hardware source. It will sync to the incoming tempo and its internal sequencer will respond to incoming MIDI start, position, and stop messages.
Note: In this mode, the Refraktions sequencer will not move until it receives a start command from an external MIDI source.
Send MIDI Clock
Refraktions outputs a MIDI timing clock at the tempo of its internal sequencer (set by the Tempo Selector). It also sends MIDI start, stop, and position messages when the sequencer is scrubbed or reset.
None
Refraktions ignores any incoming MIDI timing clocks and does not output a MIDI timing clock.
Global MIDI Routing
This section sets the global MIDI routing for all tracks. Individual tracks can set their own routing, but these are the default sources and destinations.
Note: this section is not accessible when Audiobus is active.
Background Mode
Background Mode enables the app to continue to play music or send MIDI notes after it has been moved to the background (by pressing the Home button on your device). This is automatically turned on when Audiobus is active.
Note: this section is not accessible when Audiobus is active.
Reset AI Memory
The app's artificial intelligence has a memory that records user selections of tracks and keys. Over time, the memory gets imprinted more deeply and when generating new compositions, it chooses notes the user has favored in the past. This button wipes the AI memory clear.

Reset Tracks to Default
This button resets all tracks to their original, factory-installed settings.
Support Section
Buttons for accessing this user manual or emailing the developer.
MIDI
MIDI is the most traditional way to connect Refraktions with external synthesizers, other iOS apps, or a DAW on a computer. Refraktions can both send and receive MIDI messages, and perform a MIDI thru.
Connections consist of 3 elements:
1. MIDI source --> 2. Connection path --> 3. MIDI destination
Sending MIDI
1. MIDI Source
Refraktions can act as the MIDI source, sending sequences of generative MIDI notes to the MIDI destination. This allows screen taps on Refraktions to play sounds in an external synthesizer, other iOS apps, or a software synth on a computer. As the Refraktions' sequencer loops, it will continue to send notes to the MIDI destination. It will play and morph indefinitely.
2. Connection Path
MIDI notes can travel from Refraktions to the MIDI destinations via several paths.
- Network Session
- A physical USB-to-MIDI cable (like the iConnect)
- Targeting a destination directly.
3. MIDI Destination
Refraktions can target destinations in Global MIDI Destinations. When a destination is selected here, all tracks with global selected in the Track MIDI Destinations with default to the global destinations.
Alternately, tracks can choose their own MIDI Destination and not use the global path. This way individual tracks can send MIDI to unique destinations.
Or each track can have its own MIDI Send Channel, so the tracks could all target the same MIDI destination, but use different channels to target different synths down the MIDI chain. By default, Track 1 is set to MIDI channel 1, Track 2 to channel 2, etc...
Here are some case examples of using Refraktions as a MIDI source:
Option 1: Control external hardware synthesizers
Refraktions --> USB-to-MIDI --> Synth 1 --> Synth 2 --> Synth 3
- Connect the iOS device to synth 1 using an adapter like iConnect*.
- Connect synth 1 MIDI thru to synth 2 MIDI in, and synth 2 MIDI thru to synth 3 MIDI in using standard MIDI cables.
- Set synth 1 to MIDI receive channel 1, synth 2 to channel 2, and synth 3 to channel 3.
- In Global MIDI Routing in Refraktions, select iCONNECT (or whichever adapter is being used) as a destination.
- In Refraktions Tracks 1-3, set the MIDI destination to global.
- In Track 1, set the MIDI channel to 1, Track 2 to channel 2, and Track 3 to channel 3.
- Start tapping Tracks 1-3 in Refraktions. Synth 1 is being played by Track 1 (top row), synth 2 is being played by Track 2 (second row), and synth 3 is being played by Track 3 (third row).
*Alternately you can connect to your DAW and use it to route the MIDI to your external synthesizers.
Option 2: Control iOS synthesizer apps
Refraktions --> Other iOS apps
- Launch the target app and enable its MIDI Receive. Please consult the app's documentation for specifics.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select the target app.
- Start tapping the Refraktions app. The other iOS app is now receiving notes from Refraktions.
- To have Refraktions continue to send MIDI while in the background, turn Background Mode on.
Option 3: Control DAW synthesizers
Refraktions --> Network Session 1 --> Computer DAW --> Software Synthesizers
- Set up a Network Session.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select "Network Session 1" as a destination.
- In your DAW, create a MIDI track and set the MIDI In to "Network Session 1."
- Start tapping the Refraktions app. The DAW MIDI track is now receiving notes from Refraktions. Consult the DAW's documentation on how to route the MIDI notes to play a software synth or sample.
Receiving MIDI
1. MIDI Source
MIDI sources like external MIDI controllers, other iOS apps, or a DAW on a computer can be used to input notes into the Refraktions sequencer loop.
2. Connection Path
MIDI notes can travel from the MIDI source to Refraktions via several paths.
- Network Session
- A physical MIDI-to-USB cable (like the iConnect)
- Targeting the "Refraktions" iOS virtual destination.
3. MIDI Destination
Refraktions can listen to MIDI sources selected in Global MIDI Sources. Tracks cannot select individual MIDI sources, but can filter the MIDI data it listens to by selecting a MIDI Receive Channel.
Here are some case examples of using Refraktions as a MIDI destination:
Option 1: Input notes from an external MIDI controller
External MIDI controller --> MIDI-to-USB --> Refraktions
- Connect the iOS device to an external synth using an adapter like iConnect*.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select iCONNECT (or whichever adapter is being used) as a MIDI source.
- Start playing the external MIDI controller to input notes into the Refraktions sequencer loop.
*Alternately you can connect to your DAW and use it to send MIDI to Refraktions.
Option 2: Input notes from other iOS apps
Other iOS apps --> Refraktions
- Turn Background Mode on.
- Launch the target app and enable its MIDI Send. Please consult the app's documentation for specifics.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select the target app as a MIDI source.
- Or you can choose "Refraktions" as a virtual destination in the other iOS app's MIDI destinations.
- Or you can set up a Network Session and choose "Network Session 1" as MIDI source in Global MIDI Routing and "Network Session 1" as a MIDI destination in the other iOS app.
- Start playing the other iOS app to input notes into the Refraktions sequencer loop.
Option 3: Input notes from a computer DAW
Computer DAW --> Network Session 1 --> Refraktions
- Set up a Network Session.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select "Network Session 1" as a source.
- In your DAW, create a MIDI track and set the MIDI Out to "Network Session 1."
- Start sending MIDI notes from your DAW. Each one will be input into the Refraktions sequencer loop.
MIDI Thru
MIDI Thru is a special connection where a MIDI source, like an external MIDI keyboard, can input notes into Refraktions. However instead of playing the internal sounds, Refraktions can "forward" the notes and play sounds on a MIDI destination like another iOS app or external synth. The Refraktions sequencer will loop the incoming notes and continue to play the MIDI destination. This set up is useful if it is easier to use an external MIDI keyboard or controller to start generative sequences than using the Refraktions touch screen.
Here is a case examples of using Refraktions and MIDI Thru:
External MIDI controller --> MIDI-to-USB --> Refraktions --> Other iOS app
- Connect the external MIDI controller to the device using an adapter like iConnect.
- Set the MIDI send channel on the controller to channel 1.
- In Global MIDI Routing, select iCONNECT.
- On Refraktions Track 1, enable both MIDI Send and MIDI Receive.
- On Refraktions Track 1, set the MIDI Receive Channel to 1.
- On Refraktions Track 1, set the MIDI Send Channel to 2*.
- On Refraktions Track 1, set the MIDI Destination to another iOS app.
- In the other app, enable MIDI receive and set the receive channel to 2*.
- Start playing the external MIDI controller. The incoming MIDI notes will enter notes into the Refraktions sequencer and play the other iOS app. As the sequencer loops, it will continue to play the other iOS app.
*In some scenarios, the other iOS app will also be listening for MIDI from the external MIDI controller. By setting the first transmission (external controller to Refraktions) to channel 1 and the second transmission (Refraktions to other iOS app) to 2, it avoids the iOS app playing its sounds twice.
Audiobus
Refraktions can be loaded as an Audio Source, a MIDI Source, and a MIDI Filter in Audiobus.
Note: When Refraktions is loaded into Audiobus, Background Mode and Ableton Link are automatically enabled. MIDI functions, including Sync, Global MIDI, and Track MIDI are not accessible since they are handled by Audiobus.
Audio Source
When Refraktions is loaded as an audio source, the internal sample playback is routed to an Audiobus audio destination.
MIDI Source
When Refraktions is loaded as a MIDI source, the sequencer's generative MIDI notes are routed to an Audiobus MIDI destination. This is a way to have Refraktions play sounds from another iOS app.
MIDI Filter
When Refraktions is loaded as a MIDI filter, a MIDI source (like an iOS keyboard) inputs notes into the Refraktions sequencer loop and instantly plays the Audiobus MIDI destination. As the Refraktions sequencer loops, it continues to play the Audiobus MIDI destination. This is the equivalent of the Refraktions MIDI thru functionality.
Ableton Link
Enable Ableton Link in the Settings Panel.
Changing the Tempo
You can change the tempo of the Link Session with the Tempo Selector. Incoming tempo requests will be displayed on the Text Display.
For more information, see the Ableton Link website.
Ideas
Real World Usage
On a personal note, I created Refraktions to be a tool to use in my own live performances and recording sessions. One of my main challenges with loop based music is finding the balance between the entranced state that rhythmic music can evoke and a composition becoming too repetitive and grating. Refraktions become my solution for that.
Live Performances
In live performances, I use Refraktions to control several of my hardware synths, including a modular set up. Refraktions takes care of the notes and sequences, evolving organically over the course of the performance. If I need to add more notes, I tap the screen. If I need to clear everything out, I reset the sequencer. But for the most part I leave it alone. I trust it to make its own composition while I'm freed up to do the fun part - turning knobs on the synths and effects pedals.
Each show is unique, a collaborative performance between myself and the AI inside the app. And each time I use it, it creates compositions that are my style. I tend to tap the lower and left areas of the screen, which are the lower-pitched synths, accented with the faster percussion hits of Track 2. The AI has learned my personal style and generates new notes that favor my preferences.
Studio Recording
In the studio, I've set up Refraktions to output MIDI sequencers into a DAW MIDI channel. I record the incoming notes for several minutes, alternately inputting notes manually and waiting to see how Refraktions morphs those sequences.
Once complete, I audition different synth sounds and samples with newly recorded MIDI notes, deleting the lackluster sections and saving the interesting ones. It's become a way to quickly generate melody and rhythmic sequences to use in a song.




















